Power load resistor
Generally, the leaded resistors tends to have higher rated power than chip resistors.
Wire-wound type CW, and metal-oxide film type MOS are available as power type resistors. Each has different electrical characteristics, which should be selected depending on circuits.
Wire-wound type applies metal resistive wire to achieve excellent stability and pulse resistant characteristics. Because resistive wire is wounded in coil shape, inductance or capacitance are relatively large and is sometimes affected by the frequency characteristics of the circuit. The product of high resistance generally tends to have long wounded resistive wire, and is more likely to be large with low resonant characteristics. Pay attention to the influence on frequency characteristics when you use wire-wound type for load resistors of voltage amplifier requiring flat frequency characteristics. In such case, non-inductive type wire-wound resistors RW_N with improved frequency characteristic, is recommended.
Metal oxide film types, by contrast to wire wound types, are smaller, better in frequency characteristics, and have higher resistance value, yet its pulse resistance inferiors slightly. Comparing the resistance range, wire wound types excel in the low range between tens of mΩ and several kΩ, while metal oxide film types cover the high range from ten's of Ω to hundreds of kΩ.
Ceramic case resistors also have wire wound types: BGR and BWR, metal-oxide film type: BSR, which should be distinguished between and appropriately used depending on the resistance range.
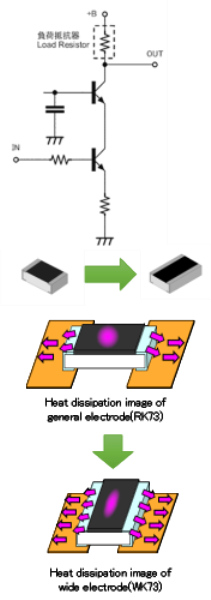
SMD types with high rated power per size include wide terminal type WK73R, WG73, WK73S and WU73 which have electrodes on the longer side. Wider electrodes on resistors achieve high rated power by lowering the thermal resistance of electrodes and improving the heat dissipation of resistors.